Blog Archive
Wednesday, November 28, 2007
Basic urinary worksheet
What are three functions of the kidneys? filters all matter from blood not just waste, selectively reabsorbs all substances that the body can make use of, eliminates waste product in blood in the form of urine
What is the protective layer around the kidney? peri-renal capsule
What is the outer layer of the kidney? cortex
What is the urine collection system of the kidney? medulla
What is the dilated end of the ureters called? pelvis
What is the function of the bladder? to store urine
What transports urine in males? Females? urethra
What is the protective layer around the kidney? peri-renal capsule
What is the outer layer of the kidney? cortex
What is the urine collection system of the kidney? medulla
What is the dilated end of the ureters called? pelvis
What is the function of the bladder? to store urine
What transports urine in males? Females? urethra
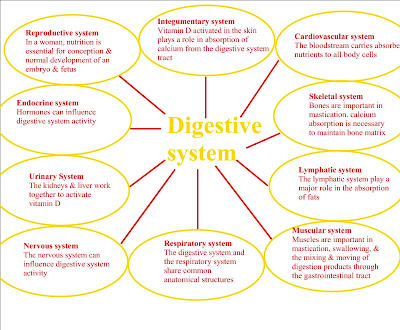
Digestive System Worksheet

What is the digestive tract? a long tube with food first entering at the mouth.
What happens to undigested materials in the digestive tract? continues along the tube until it exits at the anus.
Sketch the path that food takes through the digestive tract. Be sure to include the mouth, esophagus, stomach, duodenum, small intestine, appendix, large intestine rectum, and all 4 sphincters.
What is the function of the mouth in the digestion process? food enters through the mouth
What is the term for the small mass of food that enters into the esophagus? bolus
What triggers peristalsis?
the presence of the bolus in the esophagus triggers peristalsis.
What is the function of the cardiac sphincter? closes the entrance of stomach to prevents food from reentering the esophagus
What is the mucous membrane? digestive tract
How long is the small intestine? 20 feet
Where does most digestion and absorption of nutrients take place? small intestine
What increase the surface area of the small intestine? villi
What is the first section of the small intestine? What is its function? duodenum. the receptors can detect the presence of hypo and hypertonic solutions.
Where is bile stored? gallbladder
What is segmentation? Grabbing a tube tightly at various places around the middle and squeezing so that its contents are broken into smaller pieces.
When does the ileocecal sphincter open? when the amount of food in the small intestine begins to build up, the sphincter opens to let it through.
What is the function of the anal sphincter? stops waste from leaving the body until you want it to.
What is the function of the appendix in humans? serves no apparent function and sometimes gets infected and has to removed.
Where does digestion begin? mouth
What is gastric juice made of? hydrochloric acid, and enzymes
Where are enzymes released in the small intestine produced? Pancreas
What is the function of the following enzymes: amylase, lactase, maltase, sucrase, and lipase? they break apart lactose, maltose and sucrose respectively
There are two ways that nutrients get into the blood stream. Describe each method. diffuse across the intestinal membrane and into the blood by flowing along the concentration gradient
What happens to undigested materials in the digestive tract? continues along the tube until it exits at the anus.
Sketch the path that food takes through the digestive tract. Be sure to include the mouth, esophagus, stomach, duodenum, small intestine, appendix, large intestine rectum, and all 4 sphincters.
What is the function of the mouth in the digestion process? food enters through the mouth
What is the term for the small mass of food that enters into the esophagus? bolus
What triggers peristalsis?
the presence of the bolus in the esophagus triggers peristalsis.
What is the function of the cardiac sphincter? closes the entrance of stomach to prevents food from reentering the esophagus
What is the mucous membrane? digestive tract
How long is the small intestine? 20 feet
Where does most digestion and absorption of nutrients take place? small intestine
What increase the surface area of the small intestine? villi
What is the first section of the small intestine? What is its function? duodenum. the receptors can detect the presence of hypo and hypertonic solutions.
Where is bile stored? gallbladder
What is segmentation? Grabbing a tube tightly at various places around the middle and squeezing so that its contents are broken into smaller pieces.
When does the ileocecal sphincter open? when the amount of food in the small intestine begins to build up, the sphincter opens to let it through.
What is the function of the anal sphincter? stops waste from leaving the body until you want it to.
What is the function of the appendix in humans? serves no apparent function and sometimes gets infected and has to removed.
Where does digestion begin? mouth
What is gastric juice made of? hydrochloric acid, and enzymes
Where are enzymes released in the small intestine produced? Pancreas
What is the function of the following enzymes: amylase, lactase, maltase, sucrase, and lipase? they break apart lactose, maltose and sucrose respectively
There are two ways that nutrients get into the blood stream. Describe each method. diffuse across the intestinal membrane and into the blood by flowing along the concentration gradient
Tuesday, November 27, 2007
Reproductive system vocab
corpus luteum Structuure that forms the tissue of a ruptured ovarian follicle and secretes female hormones
epididymis an elongated organ on the posterior surface of a testis that constitutes the convoluted beginning of the vas deferens.
gonad A sex cell producing organ
meiosis A form of cell division that halves the genetic material resulting in egg and sperm cells
oocyte An immature egg cell
ovary The primary reprodutive organ of a female
placenta Structure attaching a fetus to the uterine wall providing a conduit to recieve nutrients and excrete wastes.
scrotum Apouch of skin that encloses the testes.
seminiferous tubule Tubule within the testes where sperm cells form
testis Primary reproductive organ of a male
vulva The external reproductive parts of the female that surround the opening of the vagina
blastocyst An early stage of prenatal developement that consists of a hollow ball of cells
embryo A prenatal stage of development after germ layers form but before the rudiments of all organs are present
fetus A human embryo after eight weeks of development
implantation The embedding of a cleavage embryo in the lining of the uterus
lactation Production of milk by the mammary glands
umbilical cord Cordlike structure that connects the fetus to the placenta
yolk sac An extraembryonic membrane connected to the embryo by a long narrow tube
zygote Cell produced by the fusion of an egg and sperm
ultrasound a diagnostic examination
epididymis an elongated organ on the posterior surface of a testis that constitutes the convoluted beginning of the vas deferens.
gonad A sex cell producing organ
meiosis A form of cell division that halves the genetic material resulting in egg and sperm cells
oocyte An immature egg cell
ovary The primary reprodutive organ of a female
placenta Structure attaching a fetus to the uterine wall providing a conduit to recieve nutrients and excrete wastes.
scrotum Apouch of skin that encloses the testes.
seminiferous tubule Tubule within the testes where sperm cells form
testis Primary reproductive organ of a male
vulva The external reproductive parts of the female that surround the opening of the vagina
blastocyst An early stage of prenatal developement that consists of a hollow ball of cells
embryo A prenatal stage of development after germ layers form but before the rudiments of all organs are present
fetus A human embryo after eight weeks of development
implantation The embedding of a cleavage embryo in the lining of the uterus
lactation Production of milk by the mammary glands
umbilical cord Cordlike structure that connects the fetus to the placenta
yolk sac An extraembryonic membrane connected to the embryo by a long narrow tube
zygote Cell produced by the fusion of an egg and sperm
ultrasound a diagnostic examination
Tuesday, November 6, 2007
Part 1 :Starter article
How does this article relate to the immune system?
Why is this article significant to you?
Does this article change your opinion or outlook on anything?
Do you agree or disagree with the article? Why or why not?
What are some suggestions to solve the problem?
Is there something that should be done differently?
Who in the world does this affect? Why or How?
This should be posted to your blog upon completion.
This article explains how viruses change and why doctors and scientists a have to come uo with a new vaccine every year for the viruses. Scientist have to come up with different year because viruses never stay the same they are always changing. I feel that this info is very helpful for example the flu virus it constantly changes and so are vaccines it lets us know that we should get vaccinated for this every year.
Why is this article significant to you?
Does this article change your opinion or outlook on anything?
Do you agree or disagree with the article? Why or why not?
What are some suggestions to solve the problem?
Is there something that should be done differently?
Who in the world does this affect? Why or How?
This should be posted to your blog upon completion.
This article explains how viruses change and why doctors and scientists a have to come uo with a new vaccine every year for the viruses. Scientist have to come up with different year because viruses never stay the same they are always changing. I feel that this info is very helpful for example the flu virus it constantly changes and so are vaccines it lets us know that we should get vaccinated for this every year.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)